Beautiful confirm window with React
… and check why 5600+ Rails engineers read also this
Beautiful confirm window with React
When designing your web application, you would like the user to confirm some actions sometimes. For example, you may want the user to confirm deletion of his data. There is window.confirm JavaScript method that might be useful in this case but it could not be styled and just displays native browser’s dialog window. In this article I would like to show you how to create React component as a replacement for window.confirm that can have similar behaviour and your application’s look & feel. It has similar API to window.confirm so migration should be really easy.
Getting started
In this article I am using the latest React (0.13.2) and Bootstrap v3.3.4 for styling modal window. I am also using jQuery promises to handle confirm and abort actions.
Modal window
Let’s start with creating React component for Bootstrap-styled modal window. We will use that component later in confirm window implementation. We will create modal with backdrop and lock the whole UI under backdrop until the user clicks on confirm action button.
{div} = React.DOM
Modal = React.createClass
displayName: 'Modal'
backdrop: ->
div
className: 'modal-backdrop in'
modal: ->
div
className: 'modal in'
tabIndex: -1
role: 'dialog'
'aria-hidden': false
ref: 'modal'
style:
display: 'block'
div
className: 'modal-dialog'
div
className: 'modal-content'
@props.children
render: ->
div null,
@backdrop()
@modal()
The division with modal-backdrop will be used to cover and lock everything on the page. We would not close modal on backdrop click in this case.
Confirm modal
Now it’s time to implement the confirm dialog component. It will use Modal component created in previous step. We will add title, two buttons (confirm and abort) and optional descriptive text.
Promise = $.Deferred
{div, button, h4} = React.DOM
Confirm = React.createClass
displayName: 'Confirm'
getDefaultProps: ->
confirmLabel: 'OK'
abortLabel: 'Cancel'
abort: ->
@promise.reject()
confirm: ->
@promise.resolve()
componentDidMount: ->
@promise = new Promise()
React.findDOMNode(@refs.confirm).focus()
render: ->
React.createElement Modal, null,
div
className: 'modal-header'
h4 className: 'modal-title', @props.message
if @props.description
div
className: 'modal-body'
@props.description
div
className: 'modal-footer'
div
className: 'text-right'
button
role: 'abort'
type: 'button'
className: 'btn btn-default'
onClick: @abort
@props.abortLabel
' '
button
role: 'confirm'
type: 'button'
className: 'btn btn-primary'
ref: 'confirm'
onClick: @confirm
@props.confirmLabel
We are using promises in confirm and abort methods. If you are not familiar with the concept of promises, I recommend you read our beginners guide to jQuery Deferred and Promises. In short, using promises would allow us to asynchronously decide what code should be called after clicking confirm or abort button in our dialog window.
You can also notice we are using componentDidMount lifecycle method. This method is called right after the component was mounted (its representation was added to the DOM tree). We are creating a promise object in that method - you may not be familiar with using instance variables instead of state in react components. Since that promise has no effect on the rendering of our component, it should not be placed in state, because adding it to state would cause unnecessary calls of render method.
There is also one more line in componentDidMount - React.findDOMNode(@refs.confirm).focus(). We are using it for better UX, similar to the native window.confirm behaviour, so you can just press Enter when confirm dialog appears. You can also easily extend this component to enable aborting dialog when pressing Escape.
If you would like to know more about using React especially in your Rails application, take a look at React meets Rails book we have written.
Making it work
We have created modal and confirm dialog components. Now it’s time to make it work. We will create a method that will render our confirm dialog and return a promise. Once the promise is resolved or rejected, the dialog will be unmounted from DOM.
confirm = (message, options = {}) ->
props = $.extend({message: message}, options)
wrapper = document.body.appendChild(document.createElement('div'))
component = React.render(React.createElement(Confirm, props), wrapper)
cleanup = ->
React.unmountComponentAtNode(wrapper)
setTimeout -> wrapper.remove()
component.promise.always(cleanup).promise()
When resolving or rejecting a promise, we are unmounting the whole Confirm component to cleanup the DOM (I prefer removing nodes from DOM than just hiding them via CSS). We are also removing the wrapper node since it’s not needed anymore after the dialog is closed - each time we call the confirm method, new wrapper node would be created and added to DOM (you may also create a confirm target node upfront - then you would only need to mount and unmount the component in confirm).
OK, we have now all parts of our window.confirm replacement. How to use it in your code? Very simple, you should only change your conditional:
if confirm('Are you sure?')
handleConfirmed()
else
handleAborted()
that would produce something like this:
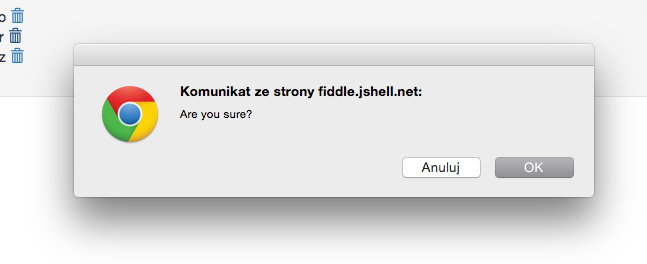
to promise version:
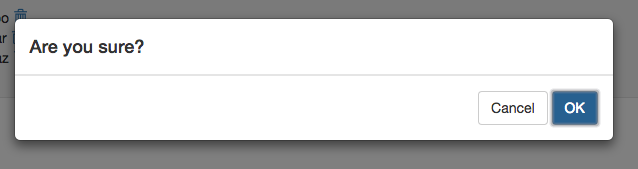
confirm('Are you sure?')
.then -> handleConfirmed()
.fail -> handleAborted()
that looks like this:
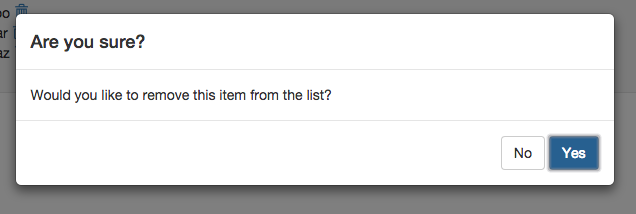
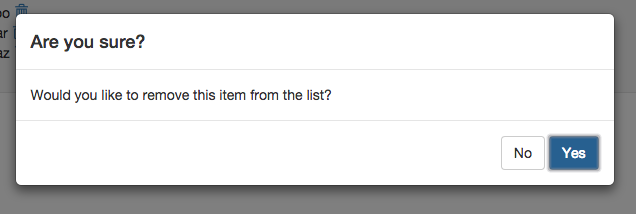
But since we have a React component, you can add more descriptive information to your confirm dialog or change button labels (with window.confirm you can only set description, the dialog title is generated by your browser):
confirm(
'Are you sure?',
description: 'Would you like to remove this item from the list?',
confirmLabel: 'Yes',
abortLabel: 'No'
)
.then -> handleConfirmed()
.fail -> handleAborted()
This is the final look:
Summary
Replacing native window.confirm with custom solution gives you ability to have the same behaviour but without restrictions - you can have beautifully styled dialog with custom button labels or dialog title. You can grab the demo on jsfiddle.