Building a React.js event log in a Rails admin panel
… and check why 5600+ Rails engineers read also this
Building a React.js event log in a Rails admin panel

Recently I talked with some awesome Rails developers about the Event Sourcing. We talked about introducing ES concept in a legacy Rails applications. That conversation inspired me to write a post about our experiences with the Event Sourcing. The most important thing to remember is that we don’t have to implement all blocks related to ES at the beginning (Aggregates, Read models, Denormalizers and so on). You can implement only one pattern and improve it slowly to full an Event Sourcing implementation. This strategy will involve small steps down a long road. This is how we work in the Arkency.
Example
We have experimented with the Event Sourcing in couple client’s projects. Some time ago we launched our vision of an Event Store (we call it RES) which we use in customer’s applications. It help as a lot to start Event-think during implementation. This example will show you how to simply introduce an ES in a Rails app. We will create a simple events browser. We will collect events describing user’s registration. Events will be saved to streams, each stream per user. This way we will create a simple log.
The idea is to display events to the admin of the Rails app. We treat it as a “monitoring” tool and it is also first step to use events in a Rails application.
Backend part
We start by adding a rails_event_store gem to our Gemfile (installation instructions).
Next thing is that we need some events to collect. We have to create an event class representing a user creation.
To do this we will use the class provided by our gem.
class UserCreated < RailsEventStore::Event; end
Now we need to find place to track this event. I thing that UsersController will be the best place. In the create method we build new User’s model.
As event_data we save information about user and some additional data like controller name or IP address.
class UsersController < ActionController::Base
after_filter :user_created_event, only: :create
def create
#user registration
end
def event_store
@rails_event_store_client ||= RailsEventStore::Client.new
end
private
def user_created_event
stream_name = "user_#{current_user.id}"
event_data = {
data: {
user: {
login: current_user.login
},
remote_ip: request.remote_ip,
controller: controller_name,
}
}
event_store.publish_event(UserCreated.new(event_data), stream_name)
end
end
The last thing is to implement a simple API to get information about streams and events.
class StreamBrowsersController < ApplicationController
def index
end
def get_streams
render json: RailsEventStore::EventEntity.select(:stream)
end
def get_events
render json: event_store.read_all_events(params[:stream_name])
end
end
Frontend part
Instead of using Rails views we will use React’s components. I created four components. The view structure you can see on following schema.
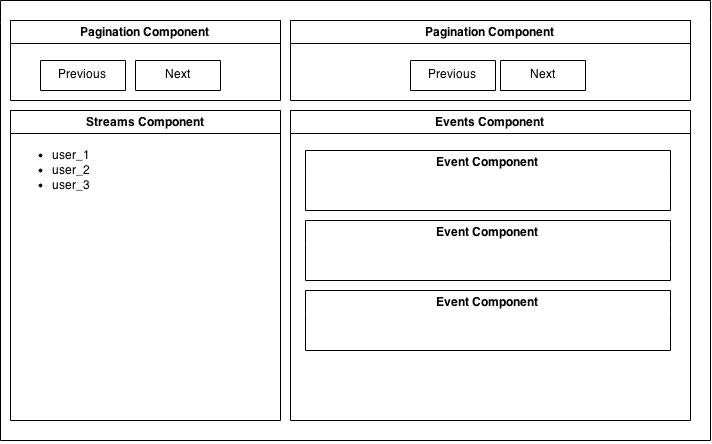
I use coffeescript to build components. As you can see on following example I use requirejs to manage them.
Recently we launched a great book about React where you can read more about our experiences with React and coffeescript.
Of course you could go with JSX as well.
define (require) ->
React = require('react')
{div, a, li, ul, nav} = React.DOM
Pagination = React.createClass
displayName: 'Paginator'
previousHandler: ->
event.preventDefault()
@props.onPrevious()
nextHandler: ->
event.preventDefault()
@props.onNext()
render: ->
nav null,
ul
className: 'pager'
li null,
a({onClick: @previousHandler, href: "#"}, 'Previous')
li null,
a({onClick: @nextHandler, href: "#"}, 'Next')
Streams = React.createClass
displayName: 'Stream'
clickHandler: ->
event.preventDefault()
@props.onClick(@props.stream)
render: ->
div null,
a({onClick: @clickHandler, href: "#"}, @props.stream)
Event = React.createClass
displayName: 'Event'
render: ->
ul
className: 'list-group'
li
className: 'list-group-item'
JSON.stringify(@props.event)
Events = React.createClass
displayName: 'Events'
render: ->
div null,
for event in @props.events
React.createElement Event,
key: event.table.event_id
event: event.table
ShowStreams = React.createClass
displayName: 'ShowStreams'
getInitialState: ->
events: []
selectedStream: null
streamsPage: 0
eventsPage: 0
onStreamsClicked: (stream_key) ->
callback = (data) =>
@setState selectedStream: stream_key, events: data, eventsPage: 0
@props.storage.get_events(stream_key, callback)
onNextStreamPage: ->
if @props.streams[@state.streamsPage + 1]
@setState streamsPage: @state.streamsPage + 1
onPreviousStreamPage: ->
if @props.streams[@state.streamsPage - 1]
@setState streamsPage: @state.streamsPage - 1
onNextEventsPage: ->
if @state.events[@state.eventsPage + 1]
@setState eventsPage: @state.eventsPage + 1
onPreviousEventsPage: ->
if @state.events[@state.eventsPage - 1]
@setState eventsPage: @state.eventsPage - 1
render: ->
div
className: 'container'
div
className: 'row'
div
className: 'col-md-4'
React.createElement Pagination,
key: 'stream_paginator'
onNext: @onNextStreamPage
onPrevious: @onPreviousStreamPage
div
className: 'col-md-8'
React.createElement Pagination,
key: 'event_paginator'
onNext: @onNextEventsPage
onPrevious: @onPreviousEventsPage
div
className: 'row'
div
className: 'col-md-4'
for val in @props.streams[@state.streamsPage]
React.createElement Streams,
key: val.stream
stream: val.stream
onClick: @onStreamsClicked
div
className: 'col-md-8'
if @state.selectedStream != null
React.createElement Events,
key: 'events'
events: @state.events[@state.eventsPage]
Last thing is to render above components on the view. I created an additional class to build the ShowStreams component and render it on the page.
I implemented it this way because we use the react-rails gem in version 0.12. In newer version you can use react_component helper to render component on server side.
This makes using easier to start with React with Rails views.
define (require) ->
React = require('react')
{ShowStreams} = require('./components')
Storage = require('./storage')
class App
run: =>
@storage = new Storage()
callback = (data) =>
mountNode = document.querySelector '.streams'
ShowStreams = React.createFactory ShowStreams
React.render(ShowStreams({streams: data, storage: @storage}), mountNode)
@storage.get_streams(callback)
= content_for :bottom_js do
:javascript
$(function() {
require(['admin/streams/app'], function(App) {
window.app = new App();
window.app.run();
})
});
.streams
The last piece of the puzzle is the Storage class. This simple class is responsible for calling the API using Ajax.
define (require) ->
class Storage
constructor: ->
get_events: (stream_key, callback) =>
$.getJSON('/admin/stream_browsers/get_events', stream_name: stream_key).done (data) =>
callback(@paginateData(data, 20)._wrapped)
get_streams: (callback) =>
$.getJSON '/admin/stream_browsers/get_streams', (data) =>
callback(@paginateData(data, 20)._wrapped)
paginateData: (data, count) ->
//this method split streams and events data into chunks. It is needed to pagination
What next?
The above example shows how simple is to introduce events in you app. For now it is only simple events log. We started to collect events related to User model.
We don’t build state from this events. Although you can use them in some Read models.
In next step you can collect all events related to User. Then you will be able to treat User as a Aggregate and build state from events.
Our other posts related to ES topic:
- http://blog.arkency.com/2015/05/building-an-event-sourced-application-using-rails-event-store/
- http://blog.arkency.com/2015/04/the-event-store-for-rails-developers/
- http://blog.arkency.com/2015/03/how-to-use-gregs-event-store-from-ruby/
- http://blog.arkency.com/2015/03/stream-pagination-in-gregs-event-store/
- http://blog.arkency.com/2015/03/your-solid-tool-for-event-sourcing-eventstore-examples/
- http://blog.arkency.com/2015/03/explaining-gregs-event-store/
- http://blog.arkency.com/2015/03/why-use-event-sourcing/
- http://blog.arkency.com/2015/03/fast-introduction-to-event-sourcing-for-ruby-programmers/